Amino Acid - Letter Code
Amino Acids
Amino acids are biologically important organic compounds containing amine (-NH2) and carboxyl (-COOH) functional groups, along with a side-chain (R group) specific to each amino acid. The key elements of an amino acid are carbon, hydrogen, oxygen, and nitrogen. When proteins are digested or broken down, amino acids are left. The human body uses amino acids to make proteins to help the body:
- Break down food
- Grow
- Repair body tissue
- Perform many other body functions
Amino Acids are classified in three groups Essential Amino Acids, Nonessential Amino Acids and Conditional Amino Acids.
Essential Amino AcidsEssential amino acids cannot be made by the body. As a result, they must come from food. The 9 essential amino acids are: histidine, isoleucine, leucine, lysine, methionine, phenylalanine, threonine, tryptophan, and valine.
Nonessential Amino AcidsNonessential means that our bodies produce an amino acid, even if we do not get it from the food we eat. Nonessential amino acids include: alanine, asparagine, aspartic acid, and glutamic acid.
Conditional Amino AcidsConditional amino acids are usually not essential, except in times of illness and stress. Conditional amino acids include: arginine, cysteine, glutamine, tyrosine, glycine, ornithine, proline, and serine.
|
| Code |
Abbrv |
Full Name |
Description |
Molecular Formula |
| A |
Ala |
Alanine |
Alanine is a non-essential amino acid. Alanine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group, and a side chain methyl group, classifying it as a nonpolar (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid.
|

|
| R |
Arg |
Arginine |
Arginine is classified as a semi-essential or conditionally essential amino acid. Arginine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
|

|
| D |
Asp |
Aspartic Acid |
Aspartic acid is classified as a semi-essential amino acid. Aspartic Acid is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
|

|
| C |
Cys |
Cysteine |
Cysteine is a semi-essential proteinogenic amino acid with the formula HO2CCH(NH2)CH2SH.
|

|
| Q |
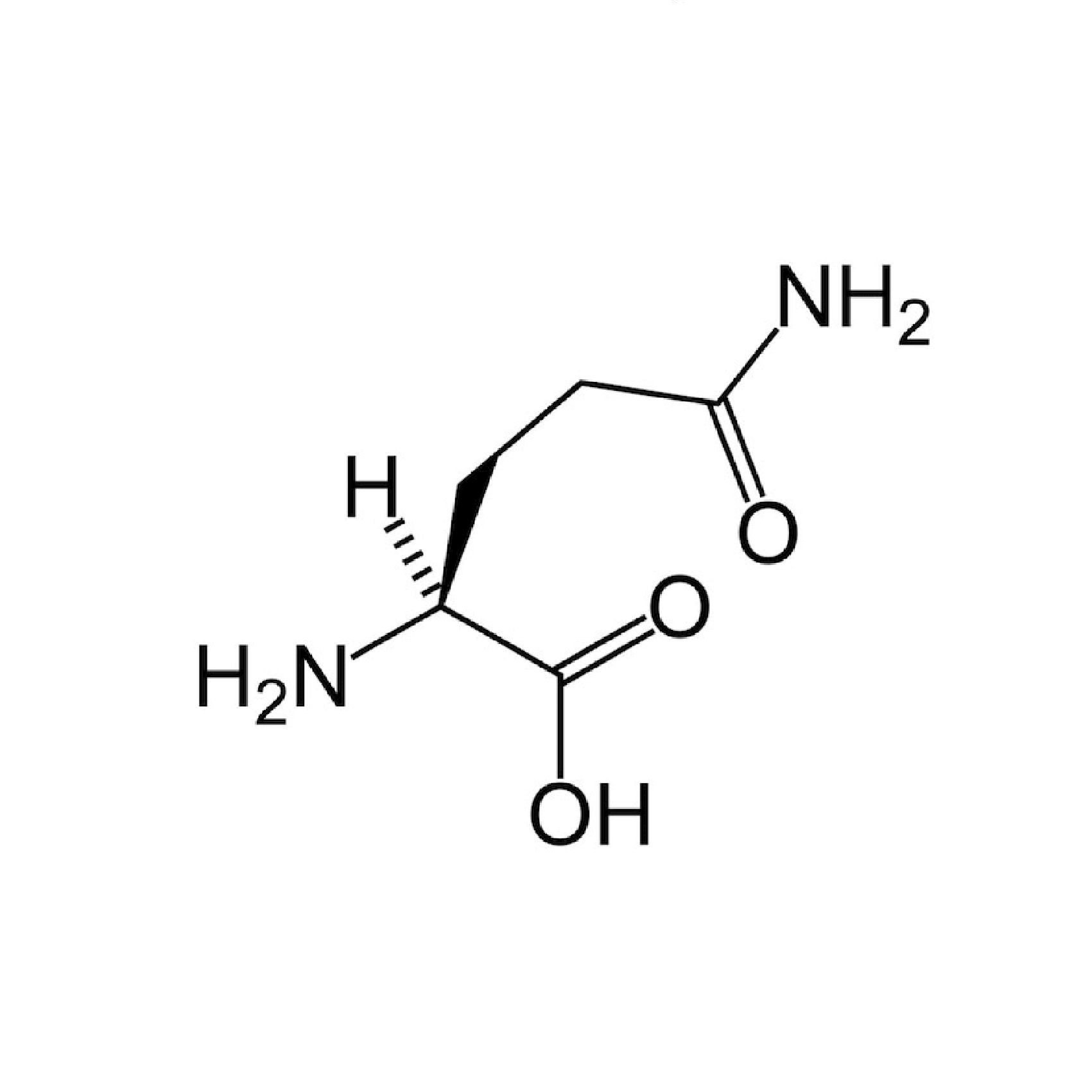
Gln |
Glutamine |
Glutamine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
|
|
| E |
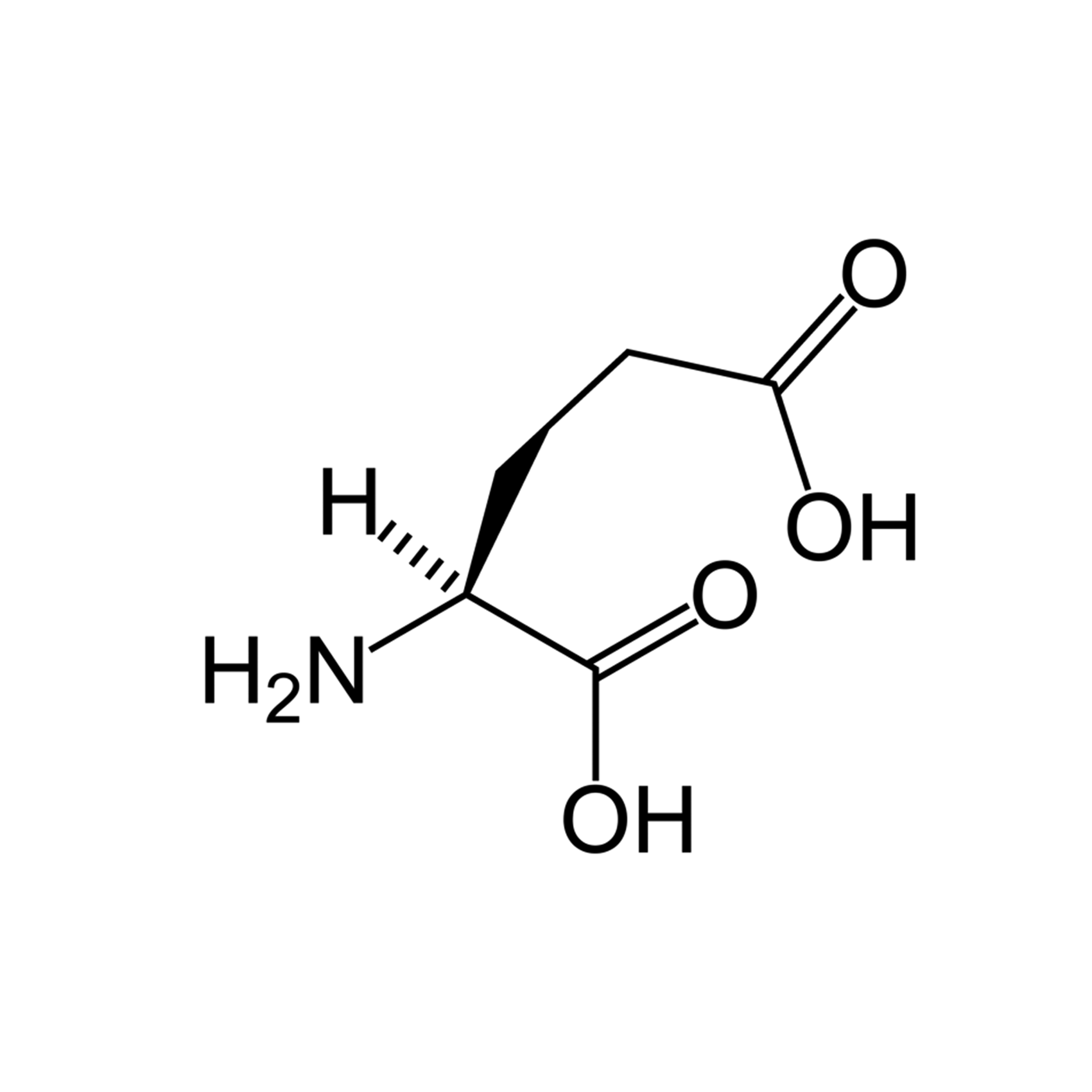
Glu |
Glutamic Acid |
Glutamic acid is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins.
|
|
| G |
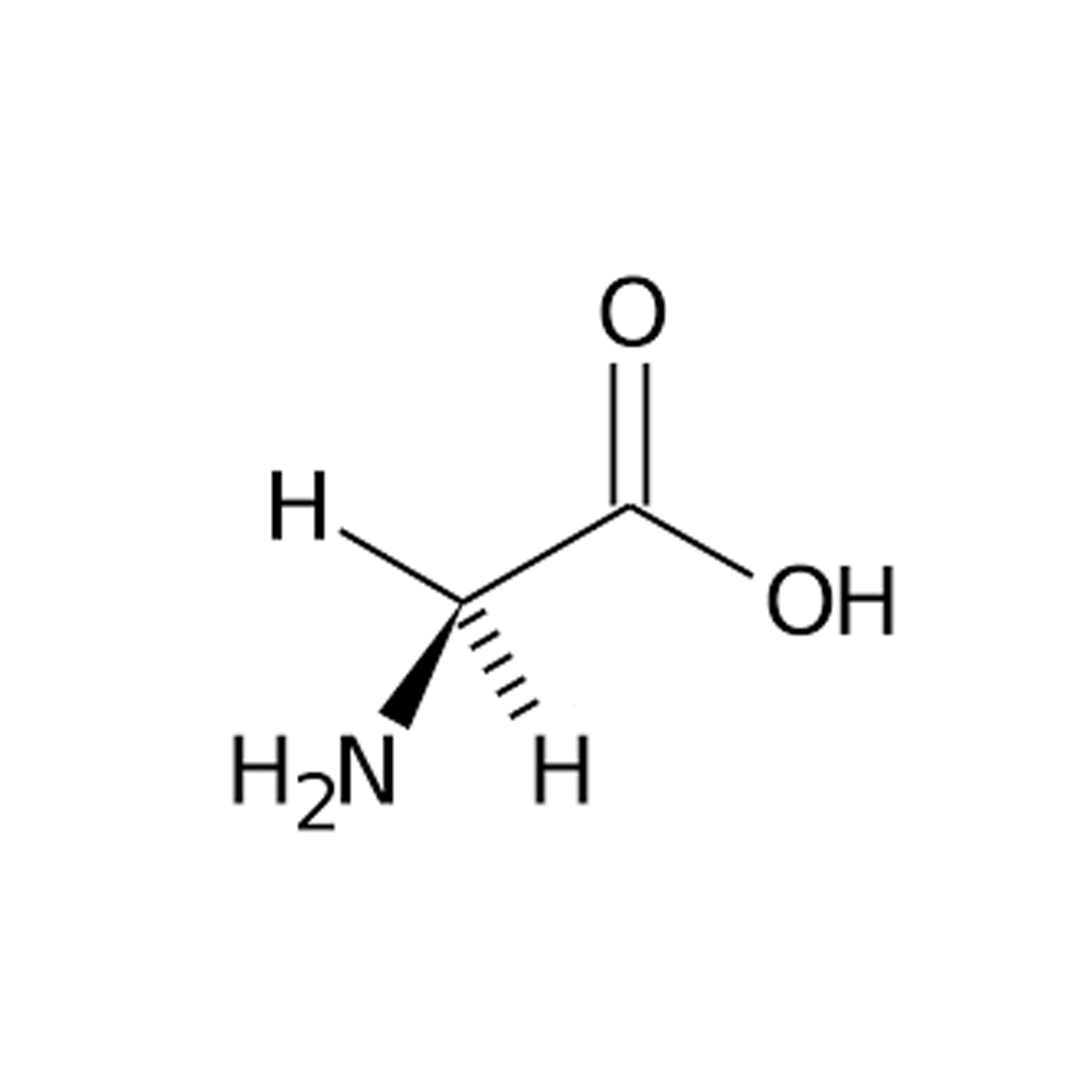
Gly |
Glycine |
Glycine is the amino acid which has hydrogen as its side chain. It is the smallest possible amino acid. The chemical formula of glycine is NH2‐CH2‐COOH. Glycine is one of the proteinogenic amino acids.
|
|
| H |
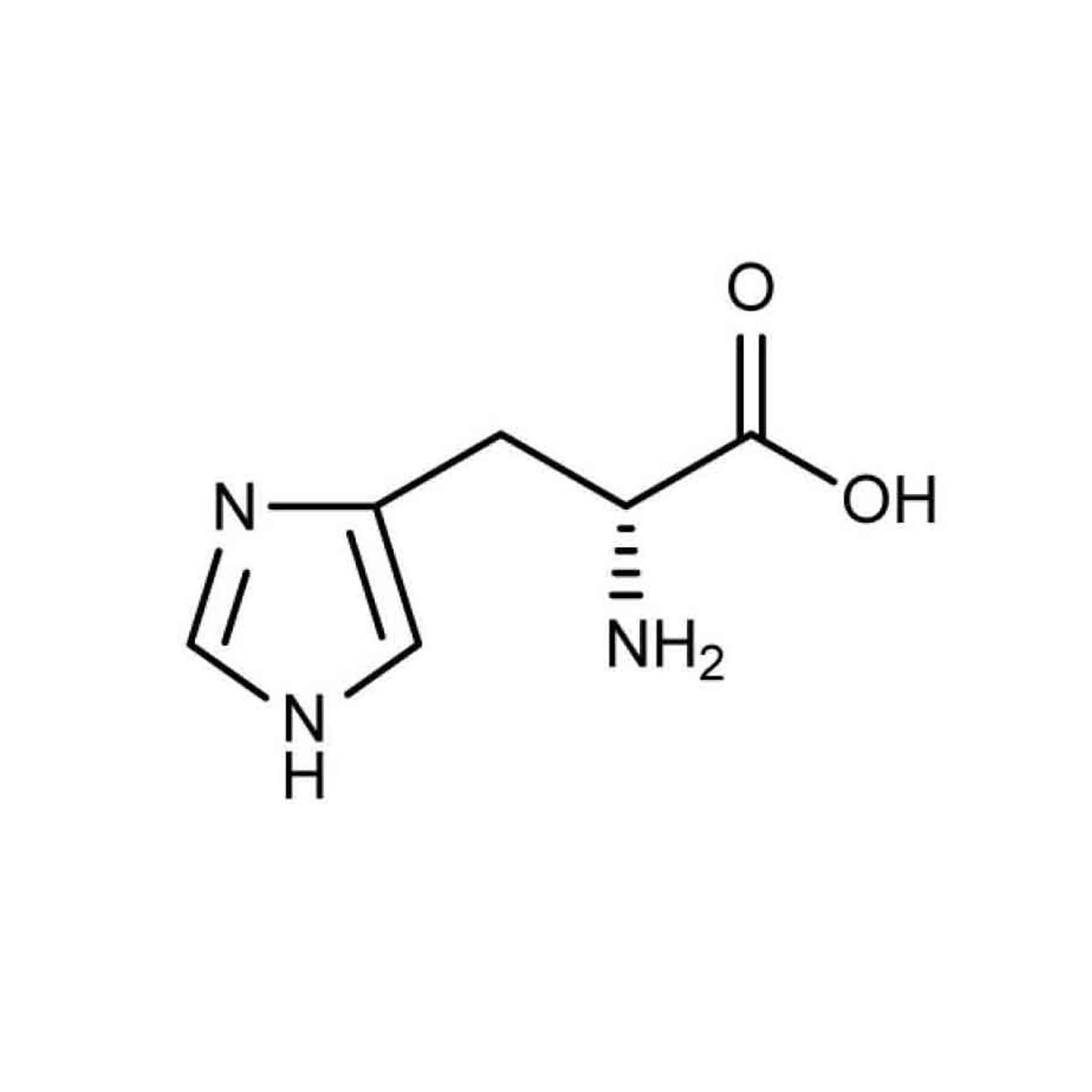
His |
Histidine |
Histidine contains an α-amino group, a carboxylic acid group and an imidazole side chain, classifying it as a positively charged amino acid at physiological pH.
|
|
| I |
Ile |
Isoleucine |
Isoleucine contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group and a hydrocarbon side chain, classifying it as a non-polar, uncharged(at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans.
|

|
| L |
Leu |
Leucine |
Leucine contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group and an isobutyl side chain, classifying it as a nonpolar (at physiological pH) amino acid. It is essential in humans.
|

|
| K |
Lys |
Lysine |
Lysine contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group and a side chain lysyl ((CH2)4NH2), classifying it as a charged (at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is essential in humans.
|

|
| M |
Met |
Methionine |
Methionine is an essential amino acid. Methionine is important in angiogenesis, the growth of new blood vessels, and supplementation may benefit those suffering from Parkinson's, drug withdrawal, schizophrenia, radiation, copper poisoning, asthma, allergies, alcoholism, or depression.
|

|
| F |
Phe |
Phenylalanine |
Phenylalanine is an α-amino acid with the formula C9H11NO2. This essential amino acid is classified as neutral, and nonpolar because of the inert and hydrophobic nature of the benzyl side chain. The L-isomer is used to biochemically form proteins, coded for by DNA.
|

|
| P |
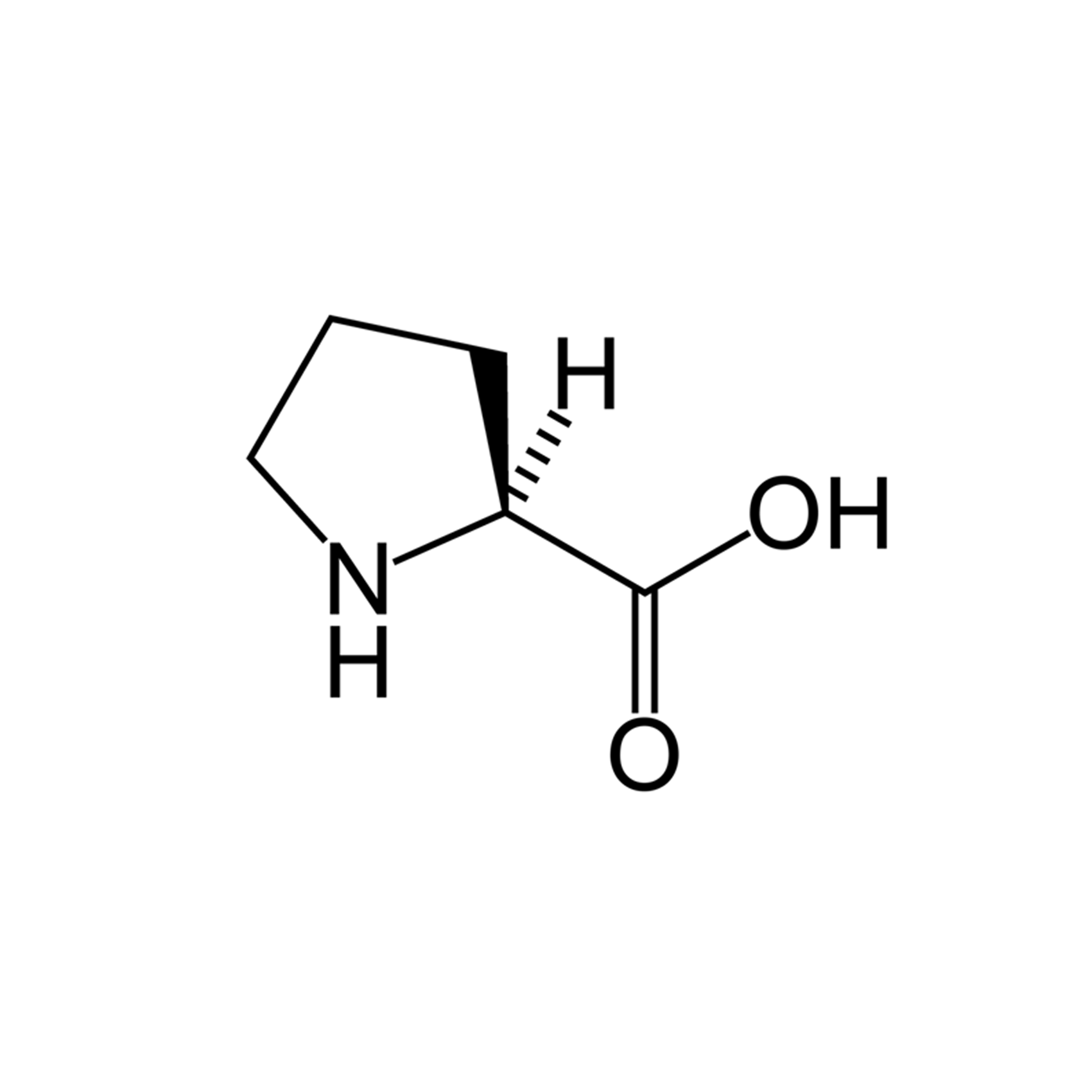
Pro |
Proline |
Proline contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group and a side chain pyrrolidine, classifying it as a nonpolar(at physiological pH), aliphatic amino acid. It is non-essential in humans.
|
|
| S |
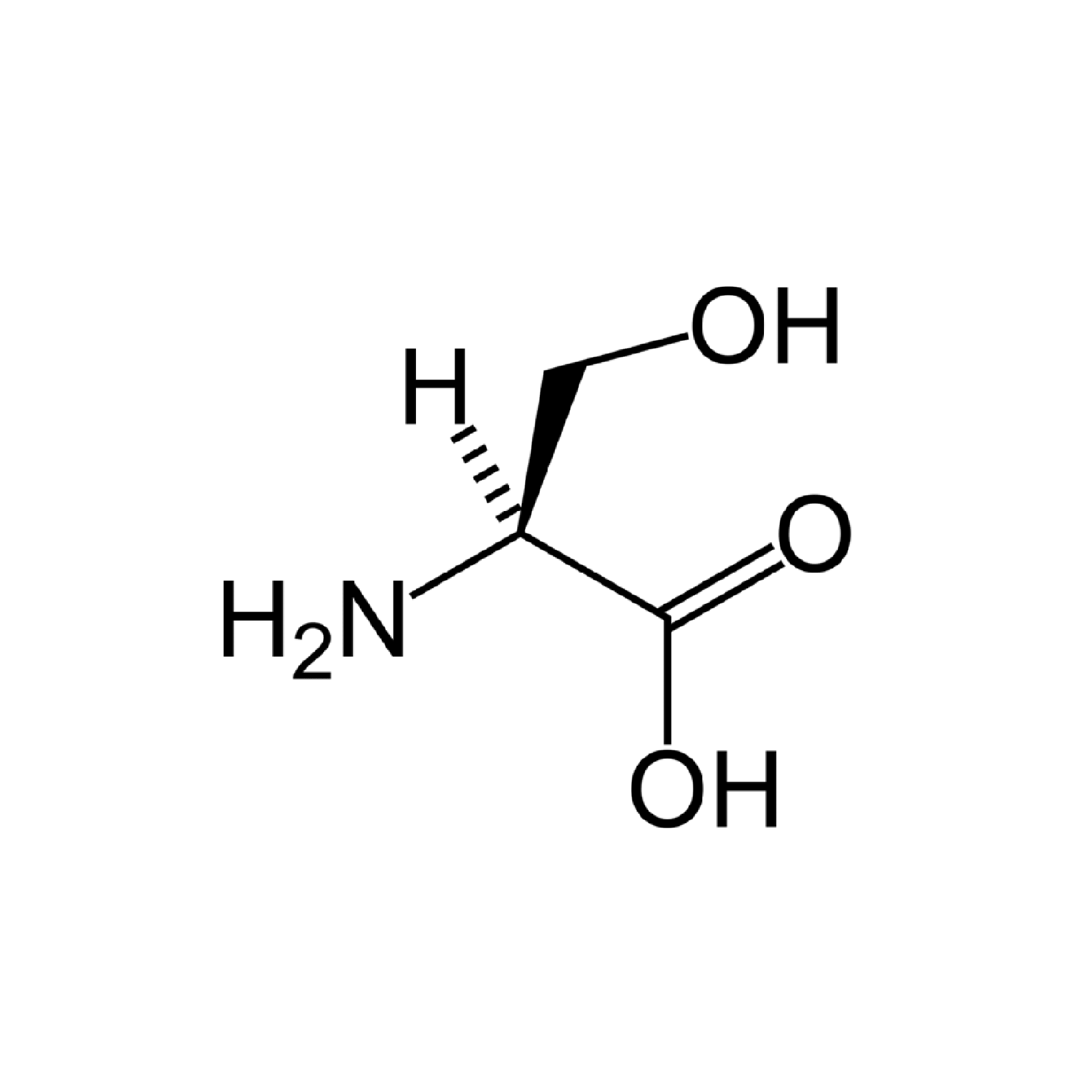
Ser |
Serine |
Serine contains an α-amino group, a carboxyl group and a side chain consisting of a hydroxymethyl group, classifying it as a polar amino acid. It is a non-essential amino acid.
|
|
| T |
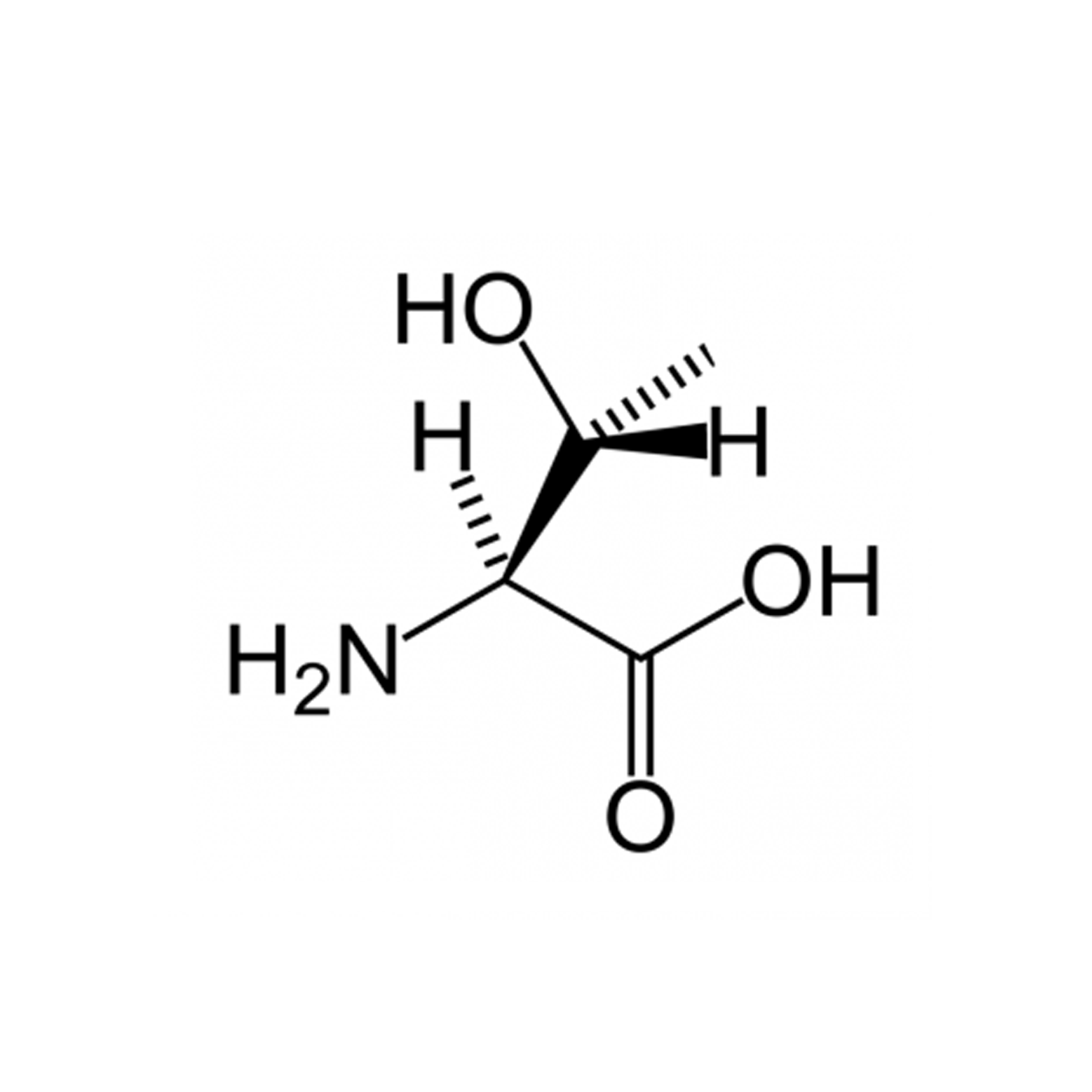
Thr |
Threonine |
Threonine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group and an alcohol containing side chain, classifying it as a polar, uncharged(at physiological pH) amino acid. It is essential in humans.
|
|
| W |
Trp |
Trptophan |
Tryptophan is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group and a side chain indole, classifying it as a non-polar, aromatic amino acid. It is essential in humans.
|

|
| Y |
Tyr |
Tyrosine |
Tyrosine is one of the 22 amino acids that are used by cells to synthesize proteins. It is a non-essential amino acid with a polar side group.
|

|
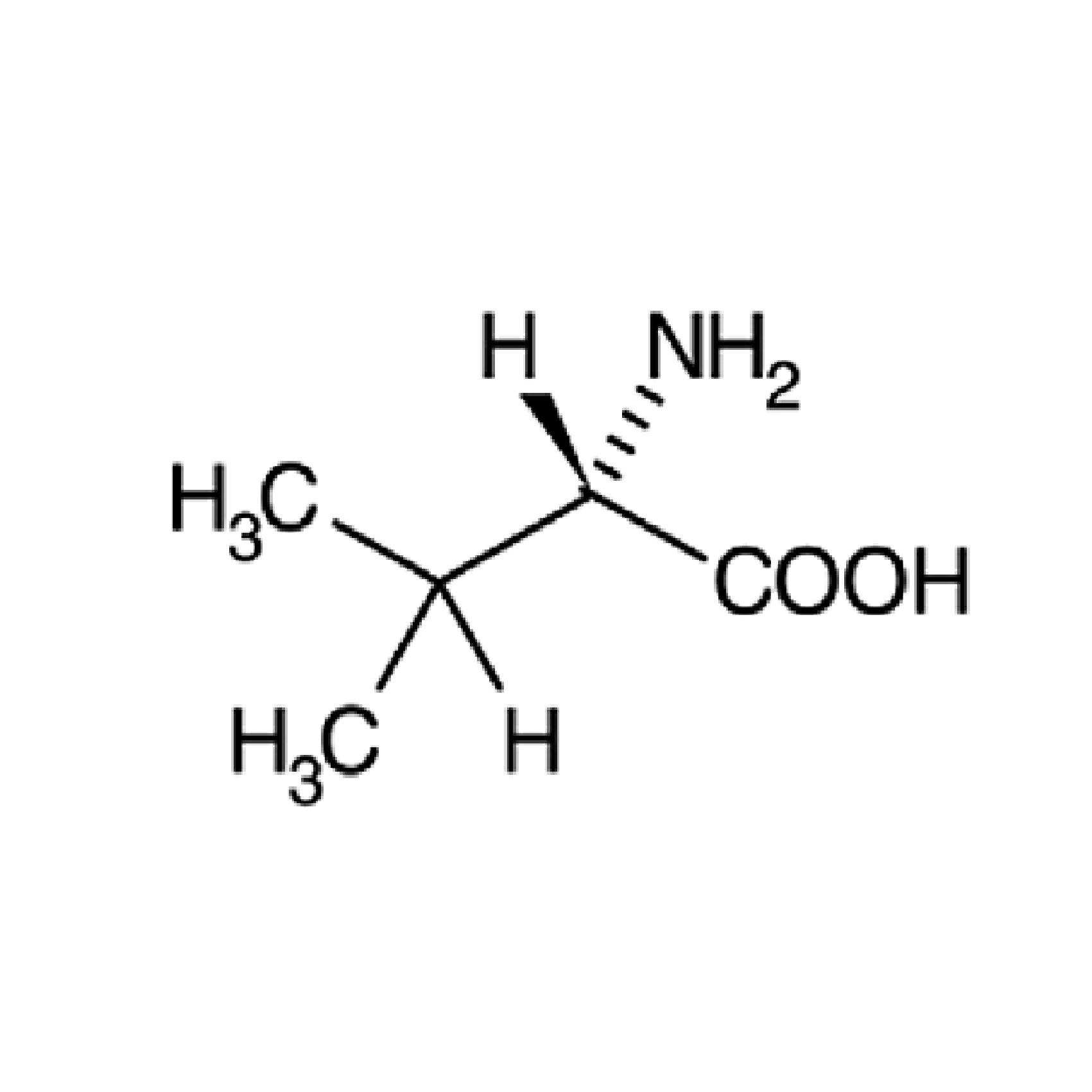
| V |
Val |
Valine |
Valine is an α-amino acid that is used in the biosynthesis of proteins. It contains an α-amino group, an α-carboxylic acid group and a side chain isopropyl variable group, classifying it as a non-polar amino acid. It is essential in humans.
|
|
|


















